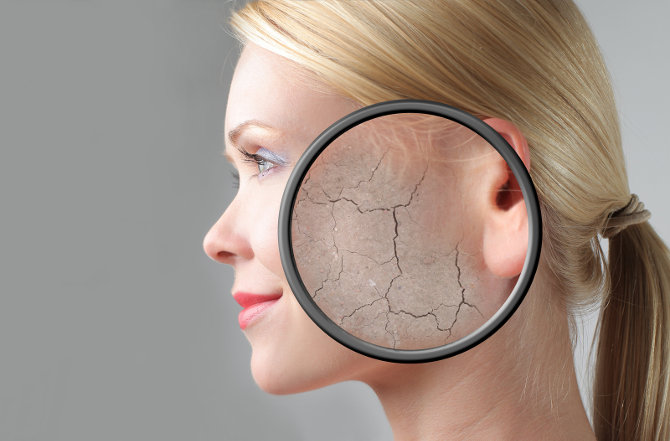
Skin Barrier Function
The Barrier Function is an extremely important concept in skin care. It describes the strength of the skin barrier and how well it protects skin from the external environment.
Like the acid mantle on the surface of skin (a physical and chemical barrier that keeps out microorganisms and irritants), the barrier function serves a crucial protective function for the skin.
The ‘Brick Wall’ Analogy
The barrier function refers to the Stratum Corneum layer of skin (outermost layer of the epidermis). It is analogous to a brick wall, a concept coined by Dr. Peter M. Elias of the University of California, San Francisco, who is an expert on skin barrier and epidermal biology.
It has a bricks and mortar structure if you look at it from a cross section: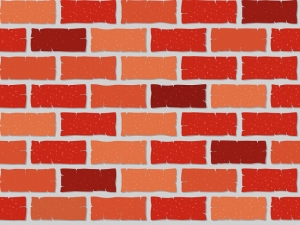
- The bricks are the corneocytes (dried out, non-living skin cells that are ready to shed).
- The mortar (cement holding the bricks together) is the intercellular matrix, which is composed of lipids (stacked lipid bilayers that surround the corneocytes).
The barrier is highly impermeable, a characteristic designed to prevent the loss of water out of skin and to prevent the entrance of harmful microorganisms or irritants.
The Importance of the Lipid Barrier
The lipids in the ‘mortar’ are responsible for maintaining skin hydration, firmness, and softness. It is commonly referred to as the lipid barrier.
The lipid barrier minimizes water loss and is essential for strong, healthy, hydrated skin. It performs 3 important functions:
- traps water molecules and prevents the passage of water out of the Stratum Corneum, which is called Transepidermal Water Loss (TEWL)
- prevents Natural Moisturizing Factors from leaching out
- prevents environmental chemicals and biological irritants from entering skin
After the age of 40, the amount of lipids decrease significantly, which is why we are more prone to dry skin as we age.
A Damaged Barrier Function
Have you ever wondered why your skin gets dry, flaky, itchy, irritated, or sensitive? These are common signs of a damaged or weakened Barrier Function.
When the lipids in the mortar are damaged or depleted by harsh products, handling, or environmental conditions, skin loses water, gets dried out, and becomes more permeable to irritants and allergens.
Once irritants or allergens penetrate the epidermis, they may trigger inflammation.
Harsh products include solvents, detergents, and irritating chemicals. Excessive use of perfumes can even weaken the barrier.
Excessive cleansing with water and soap can strip the lipids and Natural Moisturizing Factors in the Stratum Corneum, and decrease the cohesion of the skin cells.
Cleansing in hot water or exposure to steam or high heat can also strip lipids from skin.
How to Maintain A Strong Barrier Function
To have healthy, trouble-free skin, it is important to maintain a strong Barrier Function for healthy skin. It is even more important if you have sensitive skin.
1. Avoid potential irritants & allergens
2. Avoid harsh cleansers
3. Don’t exfoliate too often
4. Avoid environmental conditions that cause sensitivity (such as high heat, dry air, bitter cold, strong wind)
5. Repair the lipid barrier with barrier repair ingredients that replace lipids that are lost
6. Protect lipids from lipid peroxidation by using sunscreen regularly and an antioxidant product (serum, moisturizer) in the daytime.
There is more to come on these techniques when I cover Sensitive Skin. For now, just understand the concept of Barrier Function because it is a root cause for common skin problems, and it is not often discussed with consumers.